Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT)
Open-source intelligence (OSINT) is the collection and analysis of data gathered from publicly available sources to produce actionable intelligence. OSINT is primarily used in national security, law enforcement, and business intelligence functions and is of value to analysts who use non-sensitive intelligence in answering classified, unclassified, or proprietary intelligence requirements across the previous intelligence disciplines.
OSINT sources can be divided into several categories of information, such as:
- Media: Newspapers, magazines, radio, and televisions.
- Internet: Online publications, blogs, discussion groups, citizen media (i.e., user-created content like videos stored in mobile devices), video streaming, and social media websites. OSINT also can be collected from search engines or harvesting tools for the public internet, deep web, or even the dark web.
- Public Government Data: Public government reports, budgets, hearings, telephone directories, press conferences, websites, and speeches.
- Professional and Academic Publications: Information acquired from journals, conferences, symposia, academic papers, dissertations, etc.
- Commercial Data: Information from commercial imagery, financial and industrial assessments, and databases.
- Gray literature: Technical reports, preprints, patents, working papers, business documents, unpublished works, and newsletters.
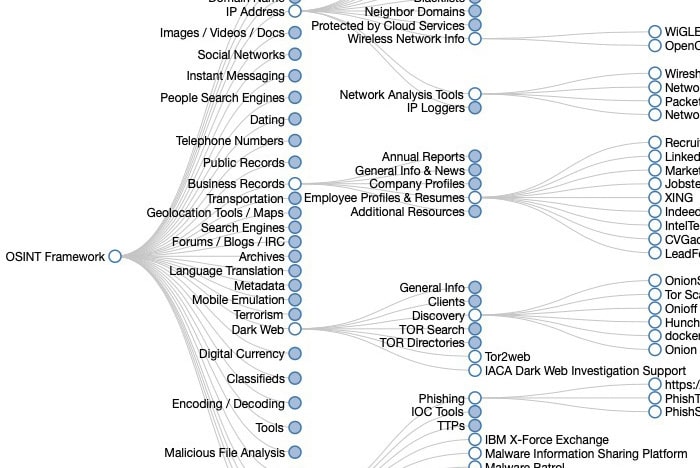
OSINT Framework is a good place to start exploring OSINT tools.
Through the web-based interface, you can access all the tools you need to get the information you need. The tools found here are all free. However, some require registration or offer better features in the paid version.
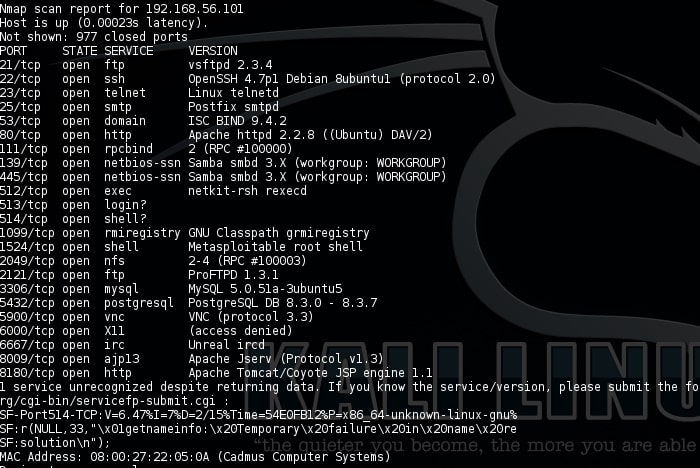
Nmap, or Network Mapper, is one of the most popular and widely used security auditing tools. It is a free and open source utility used for security auditing and network exploration across local and remote hosts. Some main features include: Host detection, IP and DNS information detection, Port detection, OS detection & Version detection.

Recon-ng is a free and open source tool available on GitHub. Its interface is easy to use and has an interactive help function (lacking in many Python modules), which allows developers to work with it straight away. Recon-ng automates time-intensive and repetitive OSINT tasks (like copy-and-paste marathons) so there is more time for the things that need to be done manually. Python beginners can use Recon-ng because it has a modular framework with several integrated features such as standardising output, interacting with databases, triggering web requests, or managing API keys. These makes it one of the most used tool for reconnaissance.

Google Dorks
Google Dorks can retrieve sensitive information from Google by using advanced search terms that allow users to search the index for a specific website, file type, and some interesting information from unsecured websites. Google Dorks can uncover some incredible information such as email addresses, passwords, sensitive files, website vulnerabilities, and even financial data (e.g. payment card information).

With the help of this tool, you can discover relationships between people, companies, domains, and publicly accessible information on the Web. Maltego searches several public data sources automatically. Among them are DNS queries, search engines, and social networks. Almost any publicly accessible data source can be accessed through the tool. Following the information collection, Maltego links the data and provides information regarding the hidden relationships between names, e-mail addresses, companies, and websites.
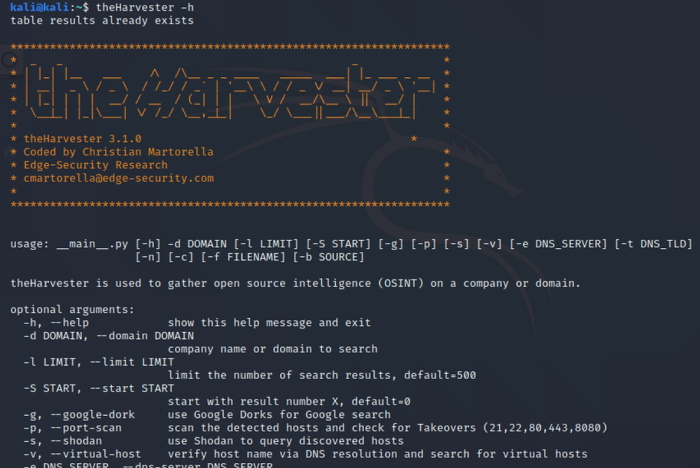
TheHarvester detects information outside of an organization's or company's own network. Despite its ability to search internal networks for information, theHarvester focuses on finding external data.
TheHarvester relies on Google and Bing, as well as the lesser known dogpile, DNSDumpster and the Exalead metadata engine as its sources. Shodan can be integrated to detect open ports on discovered hosts. In general, theHarvester captures emails, names, subdomains, IPs and URLs.
As with most free tools, theHarvester is limited as it only accesses publicly available sources and is prone to false negatives and false positives. Still, it is a good introductory tool for developers who know how to use it.
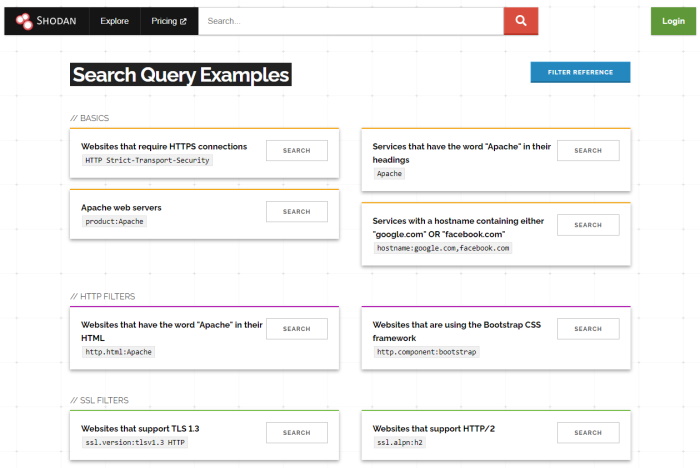
Shodan is a dedicated search engine that provides information about devices – such as the millions of IoT devices already in use. The OSINT tool can also be used to find open ports or vulnerabilities on specific systems. There are other open source intelligence tools that use Shodan as a data source - but deep interaction requires a paid subscription. Shodan is one of the few tools that includes operational technology (OT) in its analysis, such as in industrial control systems of power plants and factories. In an industry where IT and OT are intertwined, any OSINT initiative would have significant gaps unless it was built on Shodan.
Metagoofil is a free tool on GitHub. It is designed to extract metadata from public documents in various file types, such as a.pdf,.doc,.ppt or.xls file. It can link certain documents to known usernames and allow users to guess server names, shared resources and directory layouts of companies. If is often used by criminal hackers to locate information and exploit weaknesses. Thought it is not a complete OSINT tool, it does well in its function.

Social Links is a Global OSINT (Open source intelligence) vendor with HQ in the US that empowers investigators and security professionals with ground-breaking AI-powered products. Social Links products include open-source data intelligence solutions for Maltego and i2 (SL Professional) and on-premise solutions for National security and Enterprises with security operation centers (SL Private Platform).

